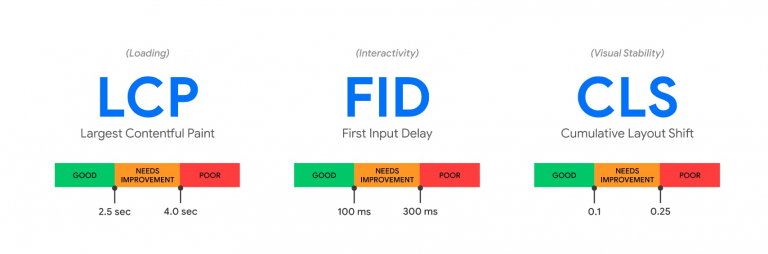
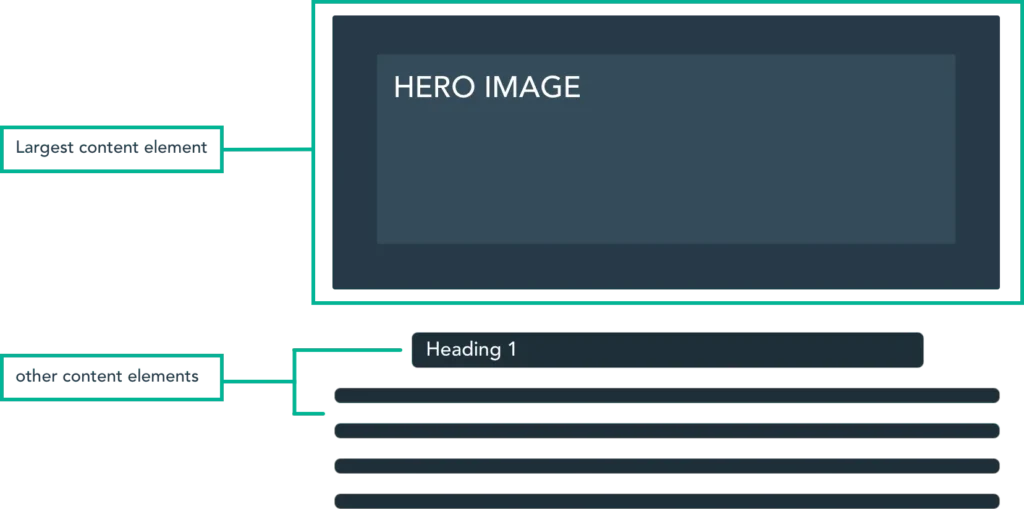
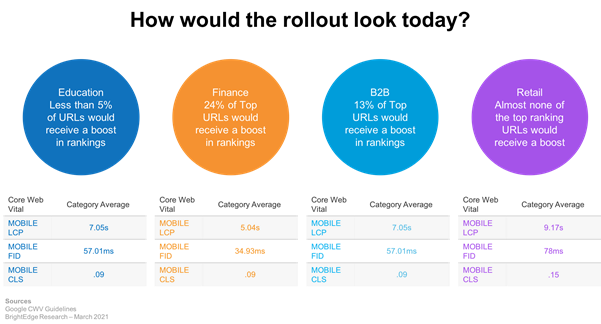
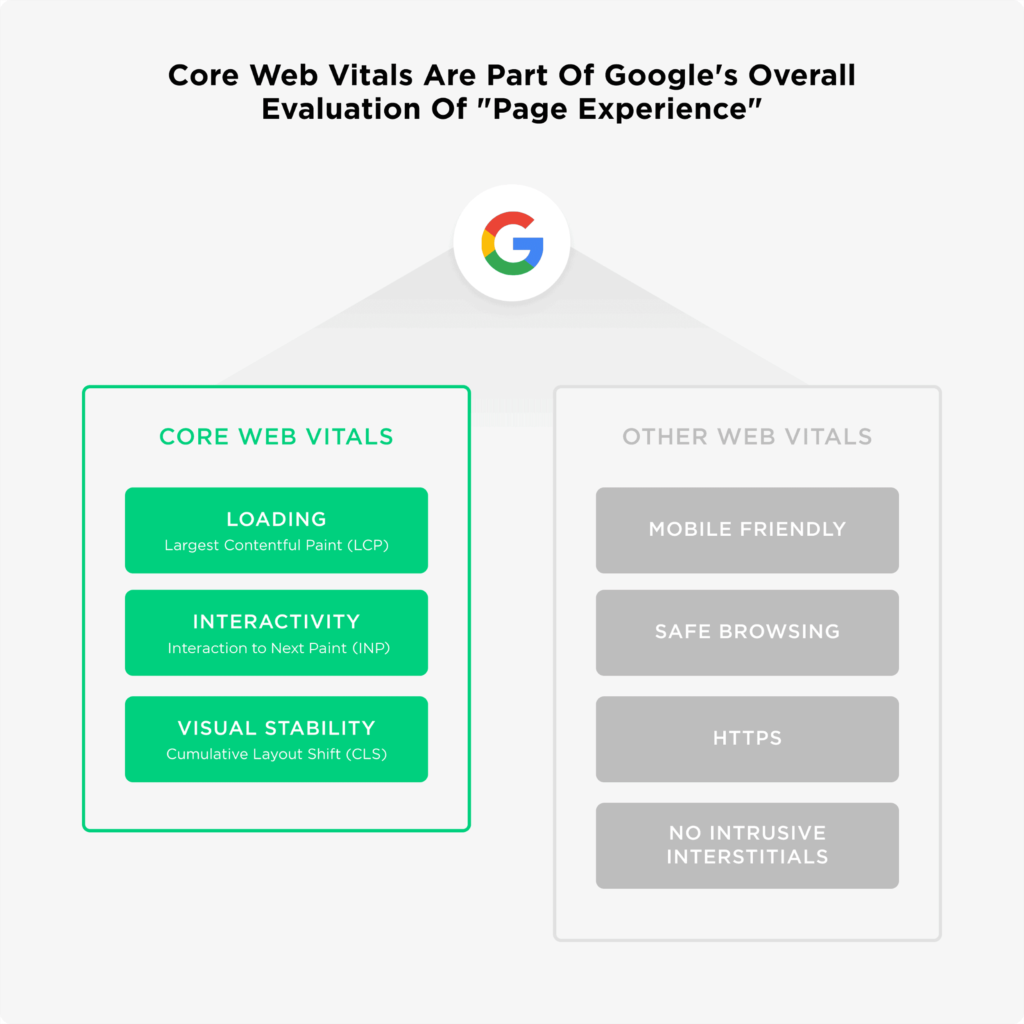
Enhancing user experience and improving SEO rankings are both significantly influenced by Core Web Vitals. By focusing on key metrics such as Largest Contentful Paint (LCP), First Input Delay (FID), and Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS), you can ensure that your website is fast, responsive, and visually stable. This focus will not only boost user satisfaction but also enhance visibility in search engine results.
For anyone aiming to improve website performance, SEO, and conversion rates, prioritizing the optimization of Core Web Vitals is essential, as Google places considerable importance on user experience in its ranking algorithms.
By implementing best practices and utilizing the right tools, you can effectively optimize your website's Core Web Vitals, thereby providing your users with a superior, faster, and more engaging online experience.